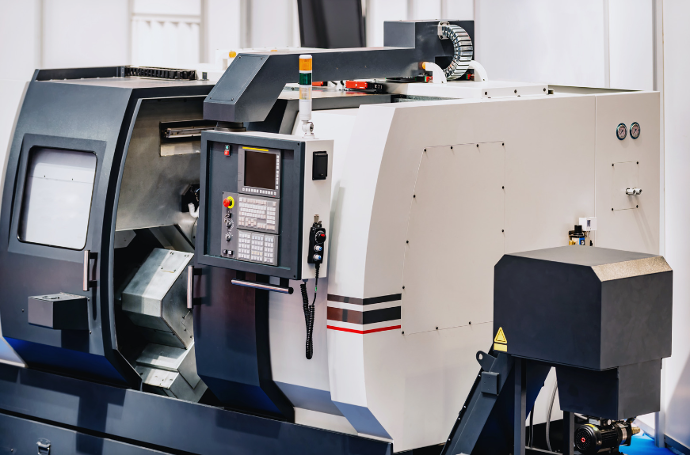

CNC Machining
CNC machining is a manufacturing process that uses computer-controlled machines to remove material from a workpiece to create a desired shape or product. CNC stands for "computer numerical control," which means that a computer program controls the movement of the machine tool, such as a lathe, mill, router, or grinder. The program contains instructions for the machine to follow, such as the path of the cutting tool and the speed and feed rates of the tool.
CNC machining is a precise and efficient method of manufacturing, with applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics. It allows for the production of complex parts with high accuracy and repeatability, as well as the ability to automate the manufacturing process for increased productivity and reduced labor costs.
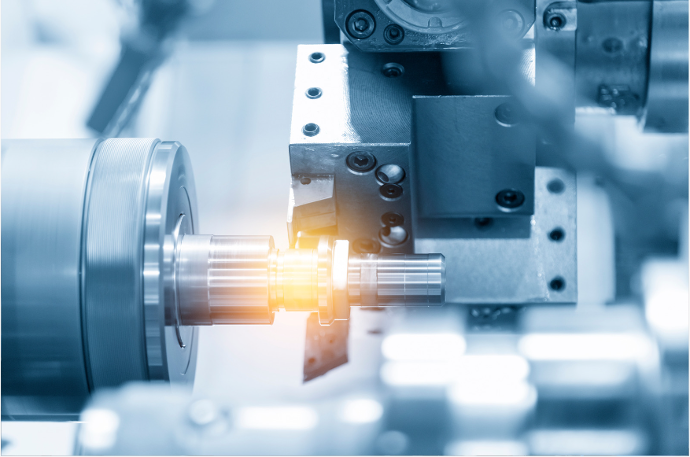
Turning Machining
During CNC turning, the workpiece is rotated at a high speed while a single-point cutting tool is moved along its surface to create the desired shape. The cutting tool can be moved along multiple axes to create complex shapes, and the depth of the cut can be adjusted for precision.
CNC turning is commonly used to create cylindrical parts such as shafts, bolts, and other rotating components used in machinery. It is a versatile and efficient machining process that can be used to produce parts with high accuracy and consistency.
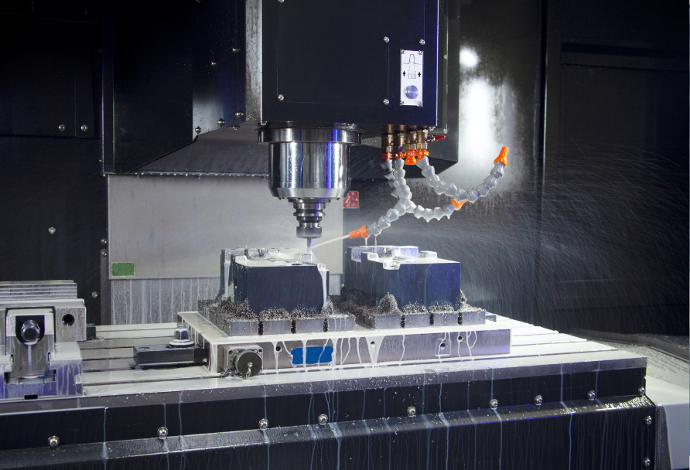
Milling Machining
CNC milling machining is a process that involves the use of computer numerical control (CNC) machines to remove material from a workpiece to create a desired shape or design. The CNC milling machine operates on a 3-axis or 5-axis system, which means that it can move the cutting tool in three or five different directions simultaneously.
In CNC milling, the workpiece is clamped onto a bed, and the cutting tool is mounted on a spindle that rotates at high speeds. The operator uses a computer program to control the movement of the cutting tool, which removes material from the workpiece to create the desired shape. The computer program is typically created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software, and the program is then converted into a language that the CNC machine can understand.